Page Contents:
Here is the Difference
Scabies and bed bug bites have similar symptoms that include skin irritation and itching.
However, because they are caused by different insects, there are some key differences to be aware of.
Scabies is caused by a microscopic mite called Sarcoptes scabiei. It is spread through close personal contact with an infected person or by sharing bedding, clothing, or other personal items with someone who has been exposed.
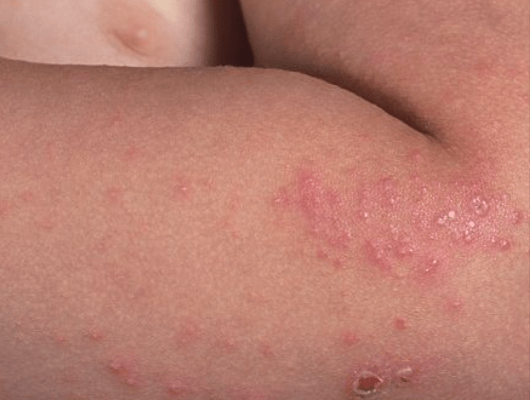
Scabies typically causes intense itching and a rash that consists of small red bumps and blisters. The rash can appear on any part of the body but is most commonly found on the hands, wrists, elbows, and waistline.
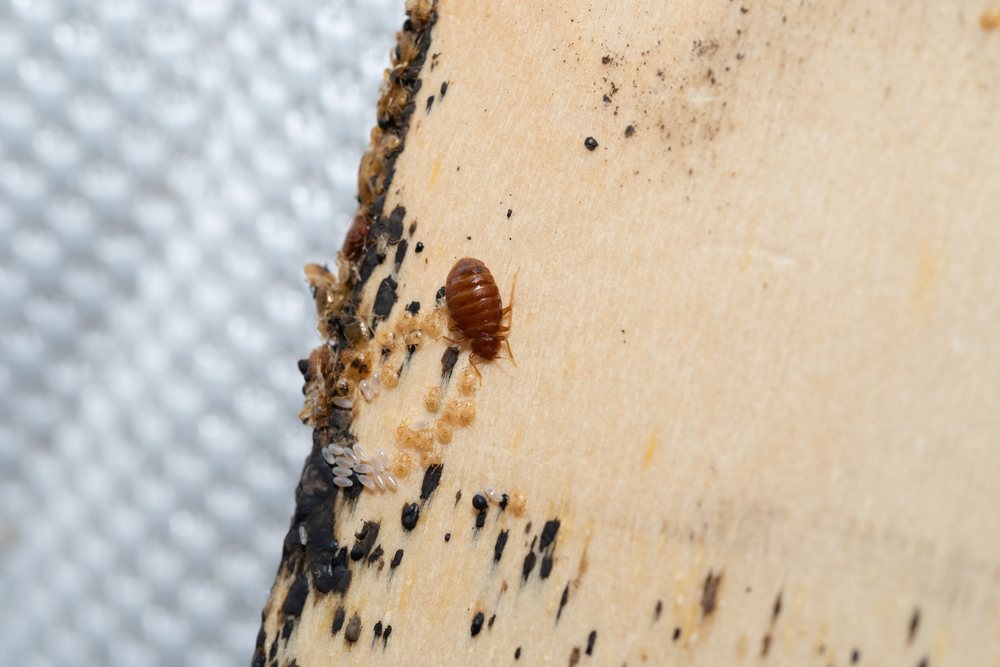
Bed bug bites, on the other hand, are caused by small, flat insects that feed on human blood. They are usually found in beds, but can also be found in furniture, dirty laundry, and other dark corners of your home.
Their bites come in the form of small red welts that can cause redness, itching, and swelling. Bed bug bites are usually in a straight line or clustered pattern on the skin, and are often found on the arms, back, legs, and other more commonly exposed areas of the body.
How to Treat Bites from Bed Bugs & Scabies
For scabies bites, the focus is on treating the underlying infected area. This is usually done with prescription medications, such as topical creams or lotions containing insecticides like permethrin or ivermectin.
These medications kill the scabies mites and their eggs.
Over-the-counter topical creams containing hydrocortisone or calamine lotion can be used to relieve the itchiness, but they do not treat the infestation itself.
It is important to note that all close contacts of the affected person should also be treated, as scabies spreads easily and is considered highly contagious.
For bed bug bites, the focus is on relieving the symptoms as these bites will heal naturally in 1 to 2 weeks.
Over-the-counter topical creams containing hydrocortisone can be used to relieve itching and inflammation. Oral antihistamines can also help to reduce itching and promote better sleep.
If the bites become infected, antibiotics may be necessary.
FAQs about Scabies
How do I know if I have Scabies?
To diagnose scabies, a doctor will first examine your skin and look for signs of the characteristic rash and burrow tracks. They may also use a handheld magnifying lens to identify the mites, eggs, or fecal matter left by the mites.
In some cases, skin scraping may be taken and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of mites or their eggs. Some doctors may also recommend treatment for close contacts of an affected person if scabies is suspected.
How is scabies spread?
Scabies is usually spread through close personal contact with an infected person. These pesky mites can also circulate through sharing clothing, bedding, or other personal items that have come into contact with an infected individual.
How is scabies diagnosed?
A diagnosis of scabies is usually made by a healthcare provider based on the characteristic symptoms and physical exam findings. In some cases, a skin scraping may be taken and examined under a microscope to confirm the diagnosis.
Can scabies be prevented?
Scabies is usually prevented by avoiding close personal contact with infected individuals and their belongings.
It is also important to avoid sharing clothing, bedding, or other personal items with anyone with scabies.
When traveling or staying in shared accommodations, inspect the bedding and furniture for signs of bed bugs or scabies before settling in. If you suspect that you have been exposed to scabies, seek medical attention immediately and take measures to prevent the mite infestation from spreading.
Facts About Scabies
1. Scabies mites can survive for up to 72 hours without a human host. Scabies mites, prefer to burrow into the skin and spread through close physical contact. However, these mites can survive for up to 72 hours on bedding, clothing, and other surfaces, making it possible for them to be transmitted even when direct contact is not made.
(Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, “Scabies”)
2. Scabies infestations are more common in crowded living situations. While anyone can contract scabies, the condition is more common in people who live in crowded or close living conditions, such as nursing homes, prisons, and college dorms.
(Source: American Academy of Dermatology, “Scabies: Diagnosis and treatment”)
3. Scabies mites do not have eyes or ears. Scabies mites are tiny, eight-legged parasites that burrow into the skin and cause a rash and significant itching. Despite their small size, scabies mites are quite complex and have a number of specialized body parts that allow them to survive and thrive on human skin. They do not have eyes or ears, which means that they rely on touch and chemical cues to navigate and find new hosts.
(Source: Medical News Today, “Scabies: Everything you need to know”)




